- Home
- Foreword
- Contents
- 1. Retrospective and perspectives
- 2. At the heart of safety: high standards and leadership
- 3. Industrial safety and radiological protection: it’s behaviours that count
- 4. Pragmatism for the EPR2
- 5. The fleet upgrade: a colossal programme
- 6. Reactors that adapt to climate change
- 7. Nuclear fuel and reactivity control: the heart of nuclear safety
- 8. Competences: are we sufficiently demanding?
- 9. Changes in the electricity system: anticipate rather than suffer
- Appendices
- Contact
Navigation
Navigation
INTRODUCTION
Marked in particular by the rise of intermittent renewable energies, the electricity system is undergoing a radical change.
While reactors have been designed to be resilient to grid events, the link between electrical system security and nuclear safety should not be underestimated.
The reduction in margins in the electricity system is leading to an increase in disturbances in power stations, all of which are stress-tests for equipment and teams.
Events in the United Kingdom and on the continent have prompted us to anticipate the risks involved and to define countermeasures.
The transformation of the energy mix has begun. It will accelerate under the pressure of public policy. The increase in electrical demand, the growth of intermittent renewable energies and their uneven distribution raise new issues for the electricity transmission system operators.
As solar and wind power are not yet contributing to the flexibility requirement, the electricity system has less and less margin. This is illustrated by the increase in significant system events (SSE) observed in France and the UK over the last five years. A number of significant incidents has prompted caution: the East-West separation of the European grid in January 2021, then the separation of the Iberian Peninsula in July 2021.
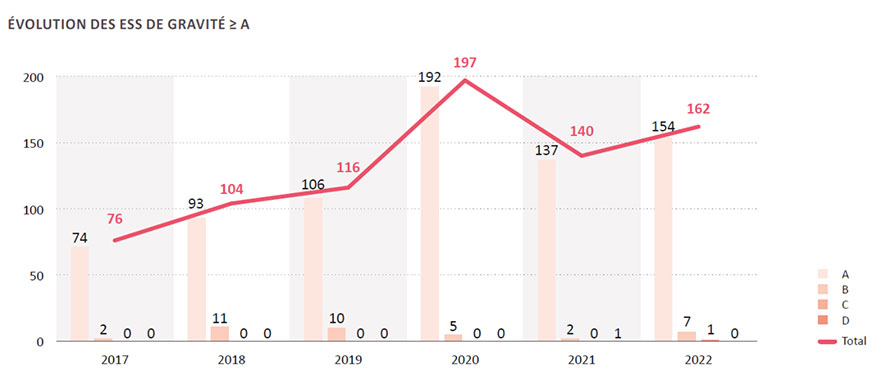
SSEs are on the rise
Every year, the French grid operator, RTE, measures the operating reliability of the power system by counting significant system events (SSE) classified according to a severity scale starting with 0 (no direct impact on system reliability) and then A to F. These events reflect the occurrence of incidents whose origins may be multiple.
With 162 SSEs, 2022 is part of an overall trend that has continued to rise since 2017.
Source: Safety Report 2022 – RTE
In this context, nuclear power, controllable and adaptable, plays an essential role. Its resilience in the face of these new disruptions must be guaranteed, and the operator must be prepared to deal with a widespread network incident, however rare. The total loss of external power supplies is integrated into the design of the power plants and in the safety cases. Except in the case of islanding (see below), safety is ensured by the diesels and thermosiphon operation before the external sources are restored. Although these situations are foreseen, from a probabilistic point of view they should not be multiplied excessively.
Separation of the European electricity grid
On 24 July 2021, the European synchronous power grid split unexpectedly into two zones due to the cascade loss of several lines located on the French-Spanish border.
The technical analysis of the event carried out afterwards by the European Network Operators Group (ENTSOE) showed that the initiating event was a fire, which caused a short-circuit on one of the two lines of the 400 kV Baixas-Gaudière link. As the reduction in transited power was not rapid enough (initial flow of almost 2,500 MW), a cascade of overloads progressively led to the loss of synchronism between the French and Spanish networks, with the final consequence of completely cutting off the Iberian Peninsula from the rest of the continental European network. Source: ENTSOE
GRID STABILITY: NUCLEAR POWER AT THE HEART OF THE EQUILIBRUM
The electricity transmission system operator (RTE in France, National Grid and Scottish Power in the UK) guarantees the security of the power system. The security of the system, intrinsically ensured by the operator (architecture, reliability, operation), is based on compliance with requirements contractually agreed upon with producers and consumers. These requirements are defined in the network codes. In France, the technical reference documentation drawn up by RTE is based on the European codes.
Since the 1990s, EDF has listed all the parameters that are important for network security and defined a set of requirements to guarantee the relevance and compliance of protection settings. The historical involvement of EDF’s General Technical Division (DTG) in this field is essential. I would encourage the maintenance and operations managers at the nuclear power plants to make better use of the training courses that DTG offers.
Maintaining the frequency
From Portugal to Ukraine, the frequency of the electricity network is synchronous around 50 Hz. The slightest imbalance between production and consumption at any point on the interconnected European system leads to a variation in frequency felt by all users. To remedy this, grid operators have introduced regulation and intervention rules. Controllable generation units, including nuclear, contribute to compensating for these variations through their frequency control systems (primary, secondary and tertiary) and their inertia. If these compensation measures are not sufficient, supply interruption or load shedding plans can be used to restore balance by disconnecting pre- identified consumers.
The closure of controllable power stations combined with the development of intermittent energy sources is tending to undermine this balance, leading to:
- Difficulty in predicting their production
- Reduction in the number of production groups capable of reacting quickly
- Loss of expansion in the event of climate hazards simultaneously affecting the whole of Europe
- A smaller proportion of naturally stabilising rotating
European reserves are required to compensate for an instantaneous power imbalance of up to 3,000 MWe. In 2023, France contributed 519 MWe to this reserve.
In exceptional circumstances, the network supplying the user may find itself momentarily isolated from the European network. In such cases, RTE gives priority to maintaining voltage, even if this means that the frequency may vary over a wider range. It is up to users to take steps to protect their installations.
Maintaining the voltage
Maintaining voltage is essential to the safe operation of the electricity system. Low voltages can overload lines, cause generation facilities to trip or even lead to widespread network collapse, as experienced in Belgium in 1982 and in western France and Japan in 1987. High voltages cause equipment to age prematurely or even their destruction.
Maintaining voltage within predefined ranges is essential for the correct operation of equipment and generators connected to the grid. Most cannot accept a voltage that deviates significantly from their design voltage.
Nuclear power makes a major contribution to permanent voltage regulation by adjusting the excitation current of the alternator. The alternator produces or consumes reactive power, which modifies the voltage at the point of injection. This effect is subsequently passed on to all neighbouring points. Unlike frequency, maintaining voltage has a local influence. Nuclear power makes a key contribution to this. In spring 2023, RTE asked the Blayais site to keep two of its reactors connected to the grid to support the voltage plan for the South-West region. This resulted in the ten-yearly outage of reactor number 2 being postponed by almost a month.
In recent years, the trend towards connecting renewable energies directly to the distribution grid and burying power lines has tended to lead to high voltage phenomena. This puts the alternators at nuclear sites closer to their operating limits and closer to the protection thresholds.

ANTICIPATE AND DON’T SUFFER
Faced with these changes and their potential consequences for system security, I believe it is crucial to anticipate possible technical issues, to define additional countermeasures, and to actively contribute to the definition of new network standards.
Strategy Department and R&D at the helm
For several years now, EDF has been carrying out prospective analyses and research programmes.
In the Strategy Department, the Group’s analysts and experts involved in CHypSE (project on strategic energy assumptions) update the energy mix scenarios every year to inform investment decisions. This very detailed work examines a number of hypotheses, in particular on the investment trajectories of different countries. Safeguarding the balance of the electricity system in the long term depends on the ability of interconnected countries to coordinate their initiatives today in line with an overall roadmap; an investment of 584 billion euros would be required to modernise the European Union’s electricity networks by 2030. We must remain cautious about our collective ability to converge towards a coherent network of systems.
In R&D, grid expertise is a well-developed skill, demonstrated in particular by high-quality simulation tools and unique test facilities. The INCREASE project aims to define the effect of the integration of renewable energies on the grid and to identify the measures to be taken for the existing fleet and the next EPR2. Low-frequency oscillation phenomena (known as sub-synchronous) initiated by powerful electrical installations (e.g. wind farms) are being studied to prevent their mechanical effects on rotating units. The EMED project deals with the electricity mix of the future and, in particular, in guaranteeing the voltage map as a function of the number of coupled nuclear units.
Contribute to regulatory developments
In terms of regulatory developments, it is important that EDF’s know- how and experience contribute to defining future requirements and their compatibility with the performance limits of generation equipment. Until now, the controllable fleet has provided most of the flexibility, whereas renewable energy producers have been subject to very few requirements. As the proportion of renewable energy sources increases, it is essential that they also play their part.
Furthermore, it is crucial that the dynamic characteristics of the grid imposed on future reactors are technologically acceptable. This is why it is important that EDF continue its involvement in drawing up European network codes and reviewing them periodically. The discussions about ROCOF (rate of change of frequency), which will tend to increase with the disappearance of highly inertial controllable production units, are a good example of this involvement. While the development of renewable energies is tending to create a high ROCOF, it is also necessary to preserve the operating margins of controllable machines, which are themselves stabilising.

MAINTAINING EQUIPMENT RELIABILITY
While we need to pay close attention to the changes taking place in the electricity system, its fragility may come first and foremost from ageing.
Today, most of the 400 kV and 225 kV equipment is the responsibility of RTE. With an average age of around 50 years, the French transmission network is one of the oldest in Europe. The wall of investment required to renew it will be a crucial issue over the next fifteen years. Certain renovations are considered urgent (e.g. risks induced by corrosion). This programme is included in the ten-year plan published by RTE in 2019.
In the nuclear power plants, the same 225 kV and 400 kV equipment has been the subject of a replacement programme for several years, under the fleet upgrade programme. In the case of transformers, the aim is to replace the TP, TS and TA poles and fit them with a monitoring system. For the transmission substations, the overhead or metal- enclosed substations need to be replaced to offset corrosion, repair SF6 gas leaks and replace ageing equipment. This asset management programme must not be compromised by financial or scheduling considerations. It is also important to respect routine and conditional maintenance to ensure that installations remain compliant over time. Each will provide the necessary reliability.
PREPARING FOR WIDESPREAD NETWORK INCIDENTS, HOWEVER RARE
RTE has an effective defence plan to deal with the warning signs of a major event. In 2022, 95% of faults were eliminated in line with expectations. Nevertheless, events continue to occur and show that exceptional combinations of adverse factors, including extreme weather conditions, could lead to a widespread blackout.
Islanding and voltage transfer, essential to rebuilding the network
RTE’s strategy for restoring all or part of the network after a widespread incident is based on nuclear plants, supplemented by hydro-electric plants. Reconstruction is based on predefined frameworks to ensure progressive resupply. Islanded nuclear reactors can restart on their own, while non-islanded reactors must receive the power they need to restart from another generation unit. In the event of a widespread network incident, EDF and RTE therefore have complementary roles: EDF undertakes to successfully island certain reactors, while RTE undertakes to guarantee voltage transfers.
During islanding, a reactor stops supplying the grid and switches to reduced power to produce the electrical energy needed for its own operation. Each reactor must carry out an islanding test every four refuelling outages, and EDF’s contractual commitment to RTE is to achieve more than 60% over a rolling four-year period. This indicator now exceeds 90%.
Each site has three voltage transfer scenarios: one internal (from reactor to reactor) and two external (e.g. from a hydro-electric dam). The frequency of external voltage transfer tests has been extended from three to six years, compensated by two simulator exercises per year per site with RTE. Delays in testing show the difficulty in bringing together the conditions for implementation between the group transmitting the voltage and the group receiving the voltage. Monitoring of this programme needs to be improved. This is one of the objectives of the Voltage Transfer and Network Restoration Steering Committee.
Storm Ciarán
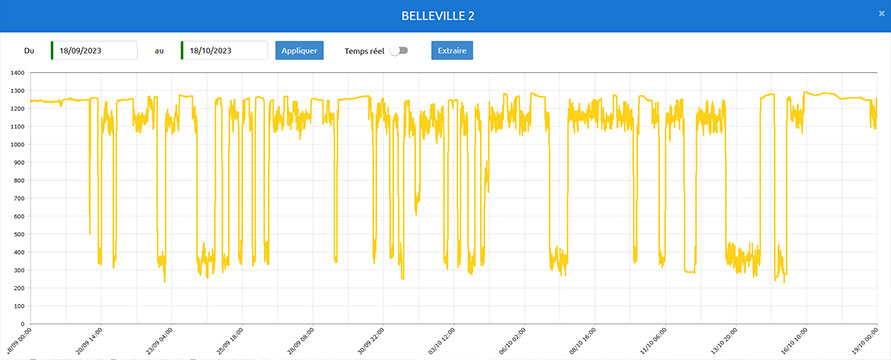
On 1 and 2 November 2023, the violent winds and heavy rain from storm Ciarán hit north-western France. Lightning struck a very high voltage line, and the wind weakened an electrical bushing on the main transformer at Flamanville reactor No. 2, leading to islanding of both units. The reactors produced the energy required by their auxiliary systems to operate independently in complete safety. The transition took place normally and was correctly managed by the shift teams. Reactor No. 1 was quickly reconnected to the grid, while Reactor No. 2 had to be shut down to replace the damaged bushing. The shift teams’ training in preparation for the event helped to manage these transients.
Strengthen theoretical and practical training
EDF’s pressurised water reactors (PWR) have robust designs, with redundancy of external, internal and ultimate electrical supplies, which have been reinforced after the Fukushima Daiichi accident (ultimate emergency back-up diesels).
The main challenge is the skills required to guarantee a high level of operational control, from 400 kV equipment to the smallest component of the electrical distribution system. From the discussions held on site and with the corporate support groups, I can see that additional efforts are needed in the areas of operations and electrical maintenance.
Operator training in this area is mainly concentrated during their initial training. I would like to encourage more widespread use of the initiative taken by some sites who organise refresher training. The aim is to ensure that, beyond the application of procedures, the teams maintain an in-depth understanding of the electrical distribution diagram and also produce diagnostic and re-supply strategies. I also think it is important that each operator regularly carry out a scenario involving the loss of external power supplies and the re-construction of the network. Lastly, the skills of the Senior Authorised Persons (SAP) in configuring and isolating 400 kV, 225 kV and 6.6 kV equipment deserve particular attention. The aim is to strengthen their knowledge and give them confidence in their ability to perform such infrequent tasks.
In maintenance, although initiatives are being taken at national level through guides and communities of practice, the risk is that they will only reach a limited number of local staff. The catalogue of training courses specific to the electrical field is well furnished (e.g., manufacturer training courses). However, everyone needs to improve their knowledge of electrical distribution. In particular, on-call electrical teams, who must work with the operator in the event of an incident, need to have a more advanced set of skills. These must be acquired through training and a development plan that includes carrying out (or observing) infrequent activities such as 400 kV or 225 kV isolations, safety train isolations or switchboard isolations. The training and development of these particular teams need to be monitored more closely.
FLEET ADAPTABILITY: AN ASSET TO BE PRESERVED
Load following is one of the strengths of EDF reactors, as other operators around the world mainly use their reactors for base load. The reactors in EDF’s fleet can vary their power between 20% and 100% in 30 minutes twice a day. Improvements to the original design make this flexibility possible.
A study carried out over the 2002-2016 period showed that load following had no obvious impact on the number of transient-related nuclear safety events or on fuel integrity, and that it had limited effects on the secondary system.
The adaptability offered by nuclear power becomes all the more essential with the priority given to renewable energies. More than ever before, we need to limit the temporary requirements for maintaining the reactor at full power to what is strictly necessary. Greater attention must also be paid to equipment that may be affected by load variations (effluent circuits, evaporators) and to the auxiliary steam boilers needed for restarting. Finally, the ability of operators to manage power transients must be a constant focus of attention.
THE UK NETWORK: CHANGES WE NEED TO LEARN FROM
The UK is aiming to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. The electricity system is undergoing major changes: the energy mix has risen from 3% of electricity generated by renewable sources in 2010 to 40% in 2022. The same period has seen the closure of conventional thermal and nuclear power stations. In this new landscape, a nuclear site may find itself the last controllable means of generation in a region, which can exacerbate the consequences of network disruption.
Events that occurred in 2023 at Nuclear Operations sites illustrate this situation.
- During a reactor shutdown, a site experienced repeated tripping of certain safety-critical electric These trips were triggered by disturbances on the network caused by a combination of unfavourable factors: the shutdown of certain lines for maintenance, power flows associated with offshore wind farms, and long-standing load imbalances on the transmission network in the region. The motor protection relays, which are too sensitive to disturbances, will have to be replaced by models that can withstand greater current imbalances.
- At another site, an automatic reactor shutdown resulted from a grid disturbance in the form of sub-synchronous oscillations (at a frequency of 8 Hz) caused by the commissioning of an offshore wind farm near the At the time of the event, the site’s alternator was the only synchronous generator connected to the grid in the region, which probably amplified the phenomenon. A modification to the alternator’s voltage regulator made it possible to address the weakness identified. Since then, the site has experienced 26 similar events, 18 of which occurred on a single day, but with no automatic trip.
Nuclear Operations has embarked on a proactive work programme. It includes the creation of periodic interface meetings with the network operator to share information, anticipate developments and define the necessary countermeasures. It also includes an equipment aspect designed to strengthen the resilience of the sites: review of minimum standards for compulsory maintenance, development of lifetime strategies for certain components, targeted investments, and improvement of the network state monitoring methods. While these initiatives are to be welcomed, they have come a little late and need to be implemented quickly. The replacement of the equipment that initiated the event in 2021 will not be completed until 2024 (see 2021 report), hence the need to analyse and deal with the equipment causes of the events in 2023 as soon as possible.

In conclusion, I encourage Nuclear Operations to take better protection against disruption from the UK grid, and the French to learn from any incidents from across the Channel, which are a precursor to what the massive arrival of renewable energy will cause on the continent.
RECOMMENDATIONS
As the changes in the electricity system and the ageing of the network place greater demands on our facilities, I recommend to the Director of the DPNT that electrical competences be reinforced and that the consequences of system disturbances on generation facilities be better managed. The maintenance and operations departments must carry out a self-assessment and address any weaknesses, with the support of the UFPI.
In response to events on the UK network in recent years, I recommend that the Director of Nuclear Operations review the settings of electrical protections to ensure that they are compliant and that their values take account of changes in the electricity system.
RECOMMENDATIONS |
As the changes in the electricity system and the ageing of the network place greater demands on our facilities, I recommend to the Director of the DPNT that electrical competences be reinforced and that the consequences of system disturbances on generation facilities be better managed. The maintenance and operations departments must carry out a self-assessment and address any weaknesses, with the support of the UFPI.
In response to events on the UK network in recent years, I recommend that the Director of Nuclear Operations review the settings of electrical protections to ensure that they are compliant and that their values take account of changes in the electricity system.